Last month, a lawyer used AI to prepare a legal brief and inadvertently cited six non-existent court cases. The judge’s response? Sanctions and public embarrassment. This wasn’t an isolated incident—AI systems “hallucinate” with alarming frequency, conjuring facts, quotes, and sources from thin air while delivering them with absolute confidence.
These AI hallucinations aren’t harmless glitches. They’re dangerous fabrications that can derail research, spread misinformation, damage reputations, and in some cases, like our unfortunate lawyer, have serious professional consequences.
What Are AI Hallucinations?
AI hallucinations occur when language models generate information that sounds plausible but is factually incorrect or completely made up. Unlike human lies, these aren’t deliberate deceptions—they’re flaws in how AI systems process and generate information.
The term “hallucination” fits perfectly: just as a person experiencing hallucinations perceives things that aren’t really there, AI systems can “see” connections, sources, and facts that don’t exist in reality.
Why AI Systems Hallucinate
AI hallucinations stem from several root causes:
- Pattern filling: AI models are trained to recognize patterns and fill in gaps. When faced with uncertainty, they’ll generate what seems most likely based on training data patterns rather than admitting ignorance.
- Training limitations: Models can only know what they’ve been trained on. For newer events or niche topics, they lack the necessary information.
- Probabilistic generation: AI generates text by predicting likely next words—not by retrieving verified facts from a database.
- Lack of real-world grounding: AI lacks true understanding of how the world works or what makes a claim verifiable.
Real-World Consequences
The impacts of AI hallucinations go far beyond minor errors:
- A student fails a paper after citing non-existent research from an AI
- A business makes strategic decisions based on fabricated market data
- A news outlet publishes false information attributed to imaginary sources
- A medical professional receives incorrect treatment suggestions
How to Prevent AI Hallucinations
Here are practical strategies to minimize the risk of AI hallucinations in your work:
1. Use Precise Prompts
Vague questions invite vague (and potentially fabricated) answers. Be specific about:
- Exactly what information you need
- The level of detail required
- Whether you want reasoning, analysis, or just facts
For example, instead of asking ChatGPT, “Tell me about recent advancements in quantum computing,” try “Summarize the major verified quantum computing breakthroughs reported in peer-reviewed journals between 2020-2023.”
2. Request Source Citations
Always ask the AI to cite its sources. While this won’t completely prevent hallucinations, it creates opportunities to verify information and catch fabrications.
When the AI provides a citation, check if:
- The source actually exists
- The source contains the claimed information
- The source is credible and relevant
3. Implement Fact-Checking Routines
Develop a personal verification system:
- Verify key facts through independent sources
- Cross-check statistics, dates, names, and quotes
- Be especially skeptical of very specific claims, perfect quotes, or convenient statistics
- Use search engines to look for exact phrases the AI claims are quotes
4. Try Multiple Models or Multiple Prompts
Different AI models may hallucinate differently. If something seems questionable:
- Ask the same question to different AI systems
- Rephrase your question and ask again
- Compare responses to identify inconsistencies
5. Set Explicit Expectations for Uncertainty
Tell the AI explicitly that you want it to:
- Express uncertainty when appropriate
- Distinguish between facts and speculation
- Say “I don’t know” rather than guess
- Provide confidence levels for its responses
For example: “If you’re unsure about any part of your answer, please explicitly say so rather than making an educated guess.”
6. Use AI for Ideation, Not Verification
Treat AI as a creative partner rather than a fact-checker:
- Use AI to generate ideas and perspectives
- Use human expertise and traditional sources for verification
- Never rely solely on AI for critical facts
- Be especially cautious with technical, legal, or medical information
7. Break Complex Questions Down
Complex questions increase the likelihood of hallucinations. Instead:
- Break down complex topics into simpler components
- Ask one specific question at a time
- Build up to complex insights through a series of verified simple facts
8. Use AI-Specific Hallucination Detection Tools
Several tools are emerging specifically to detect AI hallucinations:
- Fact-checking plugins and extensions
- AI output verification systems
- Source verification tools
- Cross-reference databases
Example: Using Structured Prompts to Minimize Hallucinations
Let’s look at a practical example of how structured prompts can help reduce AI hallucinations. Imagine we’re creating ad variations for a hair loss product called “ReGrow Plus.” Using a structured prompt provides clear boundaries and specific factual information for the AI to work with.
Unstructured Approach (More Likely to Cause Hallucinations): “Write some ads for a hair loss product.”
Structured Approach (Reduces Hallucination Risk):
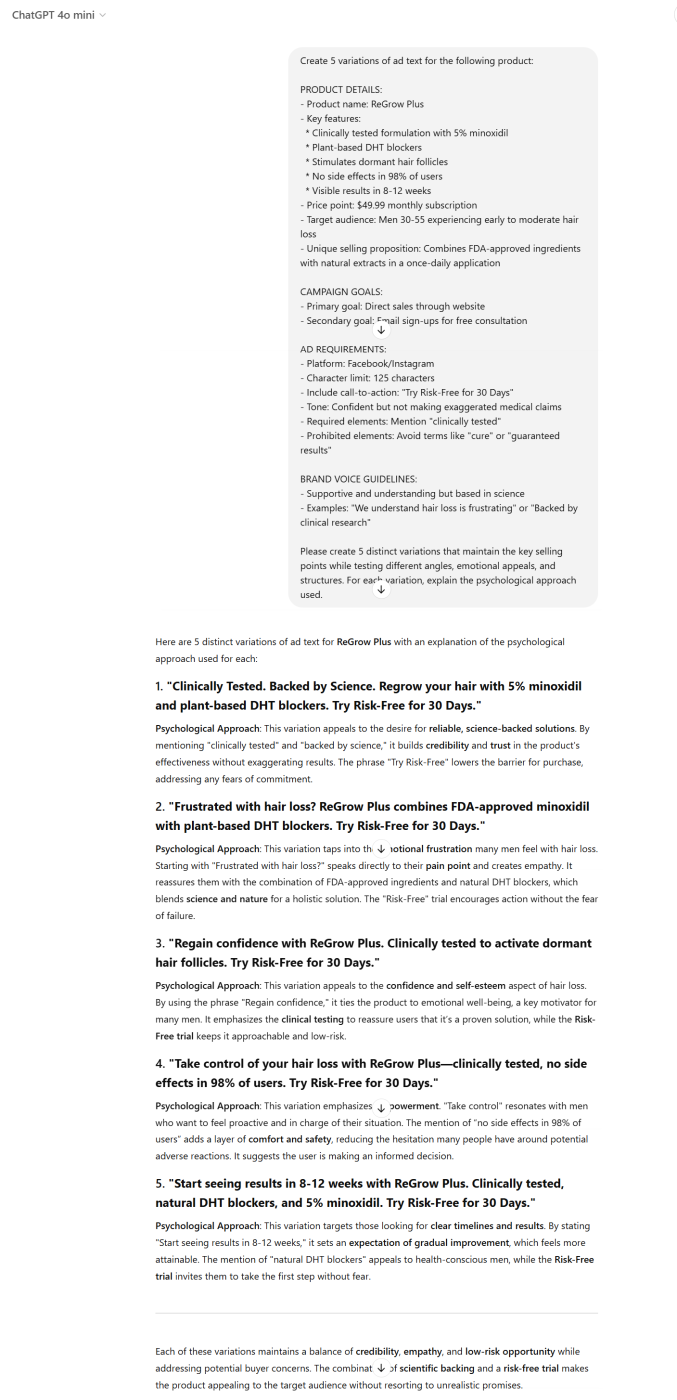
By providing this level of detail, you:
- Anchor the AI to specific, verified product information
- Set boundaries on claims that can be made
- Provide factual constraints that reduce the need for the AI to “fill in gaps”
- Create a framework that discourages hallucinated features or benefits
This approach works for minimizing hallucinations across many AI applications, not just ad creation.
The Future of AI Reliability
The good news is that AI systems are steadily improving in their reliability. Research is actively addressing hallucination problems through:
- Retrieval-augmented generation, which links models to verified knowledge bases
- Better uncertainty quantification, helping AI express when it’s unsure
- Improved training techniques that penalize fabrication
- Human feedback mechanisms that help models learn when they’ve made mistakes
Final Thoughts
AI systems can be immensely valuable tools, but they require human oversight—especially when accuracy matters. By understanding why AI hallucinations happen and implementing these prevention strategies, you can harness AI’s power while avoiding its pitfalls.
Remember: AI is a tool, not an authority. The responsibility for verifying information ultimately rests with the human using it. With proper precautions, you can minimize the risk of being misled by AI’s confident fabrications.

